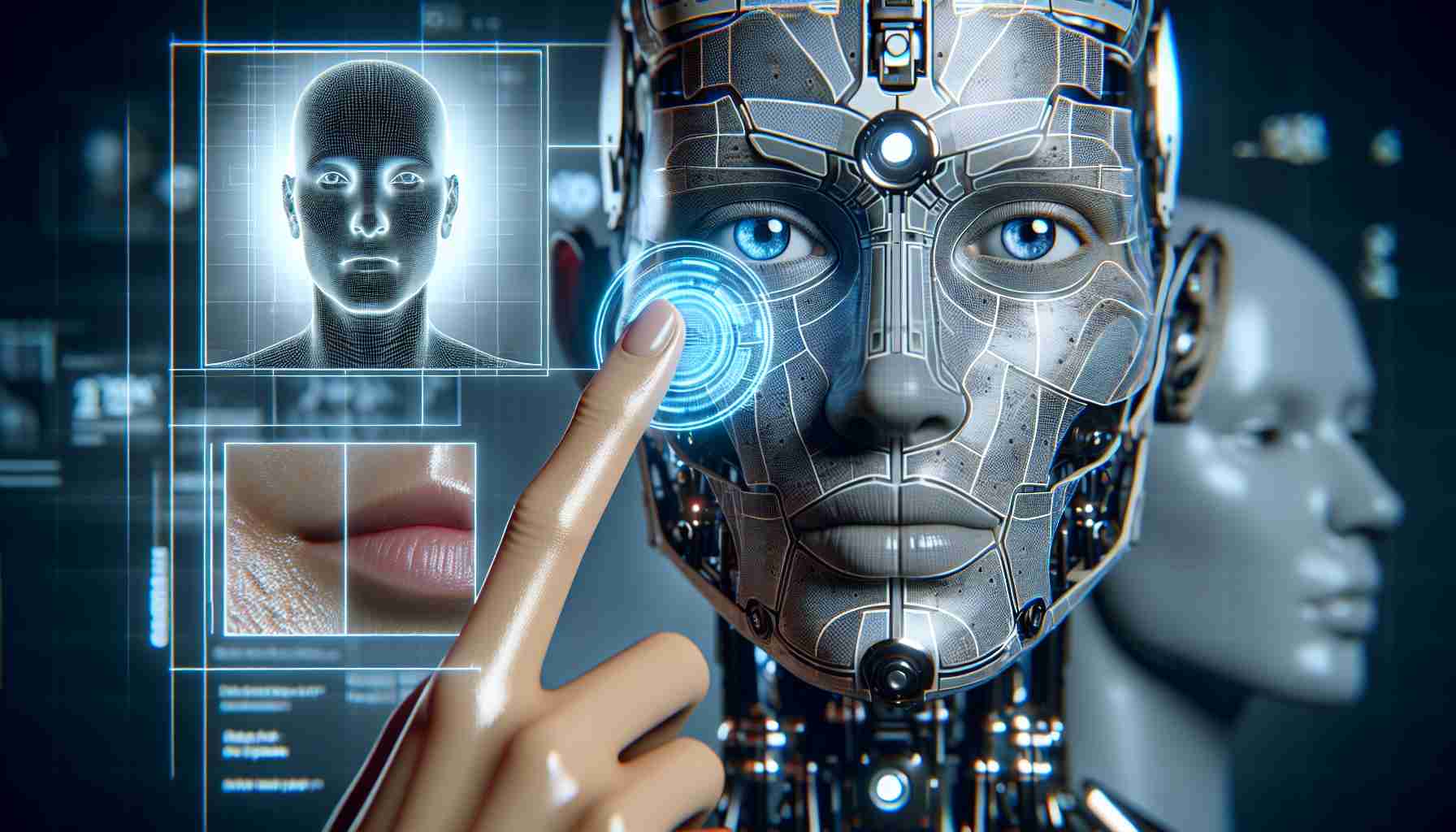
In an intriguing development, scientists have created a robot face composed of living human skin cells, marking a leap forward in how machines might interact with humans.
Researchers have grown this remarkable “skin” on a collagen scaffold, which is supported by a 3D-printed resin base. This setup allows the artificial face to possess ligament-like structures that mimic the strength and flexibility found in natural animal tissue. The innovation aims to enhance the ability of humanoid robots to communicate and express emotions more effectively, potentially revolutionizing human-robot interactions.
The Vision Behind the Living Skin: The creators of this unusual face envision a future where robots equipped with lifelike skin can better connect with humans on an emotional level, thereby improving the efficacy of robots in fields requiring nuanced human interaction, such as caregiving and customer service.
Challenges Ahead: Despite this breakthrough, the living skin currently faces limitations, with one significant drawback being its inability to survive long-term exposure to air. This challenge presents an ongoing area of research, as maintaining skin viability is crucial for its practical deployment on humanoid robots.
This pioneering work demonstrates the potential for blending biological and synthetic materials to create more lifelike robotic companions. While many technical hurdles remain, the implications for enhancing the human-robot relationship are profound, promising to bring us a step closer to a future where machines not only assist but also empathize.
Revolutionizing Human-Robot Interaction with Living Skin Technology
In a groundbreaking advancement, researchers have successfully developed a robotic face composed of living human skin cells, opening new doors for human-robot interaction.
Features and Innovations of Living Skin Technology
This innovative “living skin” is crafted from human skin cells on a collagen scaffold, mounted on a 3D-printed resin foundation. The configuration allows the artificial face to have ligament-like structures, providing strength and flexibility similar to natural tissue. Such developments hold the potential to highly enhance humanoid robots’ ability to express emotions and communicate, setting up a transformational change in the way humans interact with machines.
Use Cases and Potential Applications
With lifelike skin, humanoid robots could become more effective in roles requiring emotional intelligence and nuanced interaction, such as in caregiving environments or customer service sectors. Improved human-robot engagement may lead to better support in healthcare facilities, improving companionship for the elderly or those with disabilities and enhancing customer experiences in various industries.
Overcoming Current Challenges
Despite the promising capabilities, significant challenges persist. Notably, the living skin struggles to endure long-term exposure to air, demanding ongoing research to ensure the skin’s survivability and practical application. Resolving this limitation is crucial for robots to function effectively in real-world settings.
Insights into the Future of Integrated Biological and Synthetic Systems
The integration of biological and synthetic materials offers a glimpse into a future where the boundary between living organisms and machines becomes increasingly blurred. The potential for empathic robotic companions is immense, as the technology evolves to create machines capable of assisting and understanding human emotions.
For further exploration of innovations in robotics and AI, visit Wired for more insights into how these technologies could transform daily life.
In conclusion, while the innovation of living skin on robots ushers in myriad possibilities, the journey involves overcoming technical challenges. These advancements promise to redefine how machines interact with humans, taking a significant step toward a future where robots not only help but also empathize with humans.